Update 2025-01-27: JetBrains AI Assistant now finally supports custom OpenAI-compatible endpoints out of the box, so there’s no need for the proxying explained below. JetbBrains Junie, however, still only works with a handful of selected, proprietary models (incl. GPT 5.2-Codex, Claude Opus 4.5, Gemini 3 Pro, etc.).
Update 2025-01-26: I switched from IONOS to Scaleway in the meanwhile, because their service seems to be more actively developed further (new models being released “frequently”). Also, initial setup is easier and their cloud console UI (incl. cost management) felt more intuitive and transparent to me.
Update 2025-10-30: I updated this article to feature a simpler setup. Instead of proxying the upstream API as local Ollama endpoints, we’re using a generic, out-of-the-box local reverse proxy.
Local LLM Hosting
LLMs like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini & Co. are becoming increasingly popular among developers and even though I still prefer writing code by hand, support from an AI model still comes in handy every so often. However, I feel strongly uncomfortable with the idea of sharing my entire code base with US-based providers like OpenAI, whose data protection practices are at least questionable.
Luckily, a lot of open-source LLMs exist, including Meta’s LLaMA models, Google’s Gemma, various DeepSeek models or, lately, the Qwen model family. In addition, a whole range of amazing tools have emerged that turn self-hosting pretty much into a no-brainer, including Ollama, LM Studio and Lemonade Server.
The only downside of self-hosting a decently-sized LLM is the necessity for a lot of VRAM (check Ollama GPU Compatibility Calculator), which only pricey high-end GPUs can provide. A 20 GB AMD Radeon RX 7900 XT comes at around 700 € in Germany (used at ~ 500 €), comparable NVIDIA cards (which I’m trying to keep away from for ideological reasons and because they’re extremely overvalued) are even more expensive. Even though the recent trend towards NPU-accelerated processors that utilize shared RAM / VRAM (like the Ryzen AI 300 series or the Intel Core Ultra family) are promising for local AI inference, we’re not quite there, yet.
EU-based Model-as-a-Service Hosting
To me, the second-best option is to rely on cloud-hosted models by EU-based providers. IONOS (Germany), OVHCloud (France), Scaleway (France) and others already come with “Model-as-a-service” offerings with a per-per-use (€ / million tokens) pricing model. Note that these providers (and many more, including, netcup and ComputeBox) also offer dedicated cloud vGPU instances, but when used as an individual, they’re not being utilized efficiently, so “serverless” is the preferred way to go there.
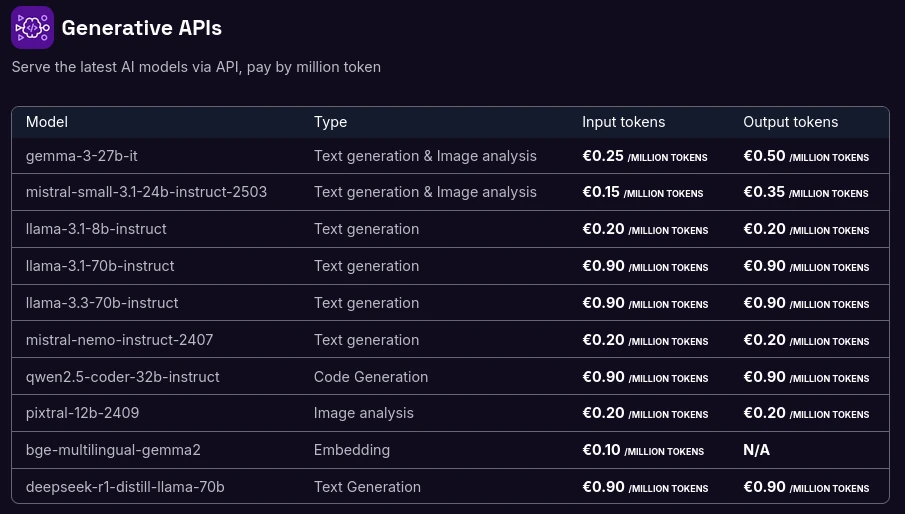
For example, for inference with a Llama 3.3 70B model, you will pay:
- ⭐️ IONOS: 0.71 € / 1M tokens
- ⭐️ OVHCloud: 0.79 € / 1M tokens
- ⭐️ Scaleway: 0.90 € / 1M tokens
- (*) DeepInfra: 0.32 $ / 1M tokens (in / out averaged)
- (*) TogetherAI: 0.54 $ / 1M tokens
- (*) LLMAPI: 2.8 $ / 1M tokens
(*) Not EU-based / GDPR-compliant, just included for reference.
Setup
I decided to give the IONOS AI Model Hub a try and opted for it as my provider of choice. They currently offer the following models, hopefully with more to come:
- Teuken 7B
- Code Llama 13B
- Llama 3.1 8B
- Llama 3.3 70B
- Llama 3.1 405B
- Mistral 7B
- Mistral Nemo 12B
- Mixtral 8x7B
- BGE m3
- BGE Large v1.5
- FLUX.1-schnell
- Stable Diffusion XL
Note that not all of these are text processing models, some are for image generation, others are only embedding models. Of the above, Llama 3.3 is probably the most promising option. Among recent open-source models, Qwen2.5-Coder or Qwen3 are known to perform even better for software development tasks, but they’re not part of IONOS current palette.
Account Creation
First steps include to create a IONOS Cloud account, sign up for the AI model hub and create an access token. Detailed instructions are provided in their tutorial. The token will later be used by your frontend (e.g. Open WebUI Nextcloud AI Assistant, VSCode, JetBrains IDE, etc.) for authentication.
OpenAI -> Ollama API Proxy
Most Model-as-a-Service solutions provide an OpenAI-compatible API, so that any tool, that can talk to an OpenAI service can also be pointed to your respective custom endpoint. However, not all code editors and IDEs currently support custom, authenticated OpenAI endpoints. There are several open issues and feature requests for JetBrains (#11585, #18360, #47) and VSCode (#7518), but until they’re implemented and upstreamed, we have to settle with a workaround. What we need is a tiny piece of middleware to proxy between the two different formats, that is, expose IONOS’ OpenAI API on localhost.
We’re using Caddy as a reverse proxy, which you can just install via your package manager. The config (provided as a Caddyfile) for proxying is this:
1 | :11434 { |
For Scaleway, the reverse proxy URL will be https://api.scaleway.ai instead.
You can then start the proxy by running:
1 | caddy run --config Caddyfile |
On Linux, you might also want to create a SystemD unit to automatically run Caddy in the background. On Windows you can achieve the same by setting up a Windows service.
Note: A previous version of this article presented a different approach where the IONOS OpenAI API was exposed as a local Ollama API using openai-ollama-proxy, but this comes with several downsides.
JetBrains Integration (PyCharm, IntelliJ, …)
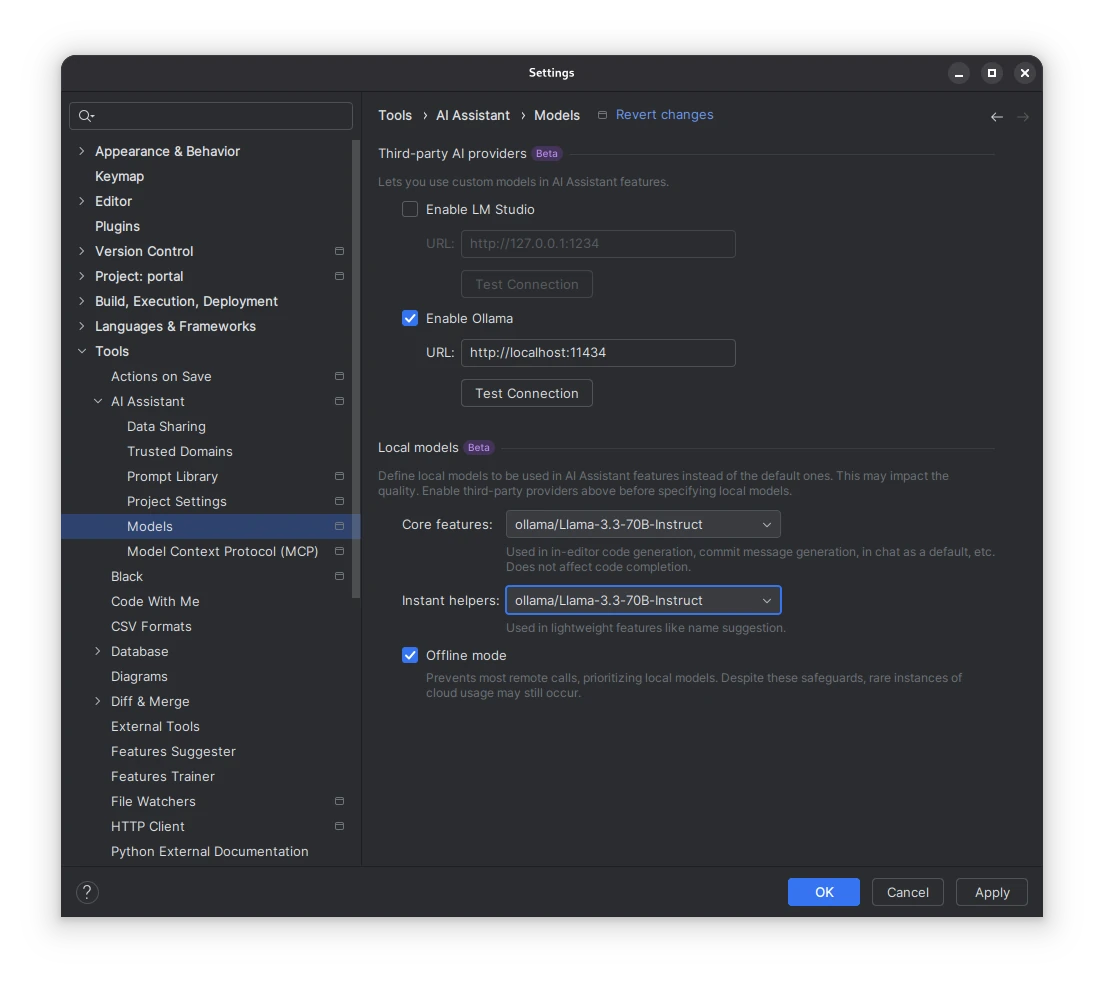
Last step is to hook up the (proxied) model with your IDE, e.g. PyCharm. To do so, enable the AI Asisstant plugin, enable OpenAI integration in its settings, choose your preferred model and turn on Offline mode. When done, you’re good to go to start chatting with Llama (or whatever model you picked) and have it help you code!
Visual Studio Code Integration
For VSCode, we’re using the GitHub Copilot Chat extension. Unfortunately, custom OpenAI endpoints are only available in the Visual Studio Code Insiders variant for now (but will hopefully make it to the “standard” edition as well).
First step is to edit the settings, which you’ll find under File -> Preferences -> Settings. Add the following snippet to hook up VScode with your reverse-proxied OpenAI API:
1 | { |
You may choose any model available at http://localhost:11434/v1/models.
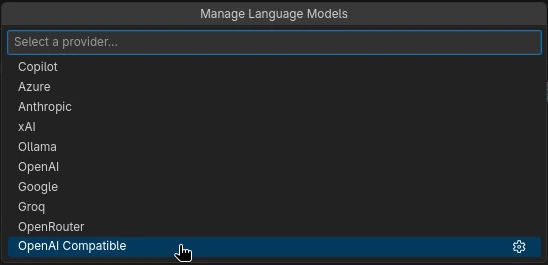
Next, bring up the Copilot chat, go to “Manage Models”, choose “OpenAI Compatible” as a provider and, if you did everything right, it will already pick up your local endpoint and list the available models.
Conclusion
If you value digital sovereignity, don’t want to purchase an expensive graphics card that would still end up idling most of the time, but nevertheless want to leverage LLM assistants for repetitive coding task, opting for EU-based model-as-a-service offering is probably a sound option for you. My above instructions may guide you on your way to a “semi-local” AI coding setup.
Alternatively, there is also Mistral LeChat as an EU-based ChatGPT alternative or FLUX.1 by Black Forest Labs for image generation.
Have fun and happy coding! ✌️
Comments